Minimal Invasive Pain Therapies
-
Splanchnic Nerves Block /Lesion
ANATOMY The pain signals from visceral organs of the upper abdomen (pancreas, liver, spleen, gall bladder, stomach, small intestine, kidney, adrenal gland) are transferred to the spinal cord and from there to the brain via the splanchnic nerves. The splanchnic nerves are three, the greater, the minor and the least, emerging from the roots of […]
-
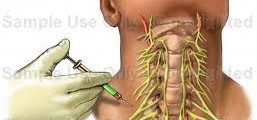
Stellate Ganglion Block
GENERAL Stellate ganglion block has a diagnostic and therapeutic value. It is applied to treat various painful conditions of the head, neck, upper extremities and upper chest. If the diagnostic block with local anaesthetic brings satisfactory analgesic result, then follows radiofrequency neurolysis of the ganglion. INDICATIONS -Acute pain due to herpes zoster -Post-herpetic neuralgia -Complex […]
-
Interventional Techniques in the Shoulder
RECOMMENDATIONS The treatment of shoulder pain should primarily be conservative with combination of pharmacotherapy and chiropractic/ physiotherapy. Should the above treatments fail (after being applied for a reasonable period of 4 weeks), minimally invasive techniques can be applied. Α. SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The patient is placed in the supine position. After thorough cleaning of the area […]
-
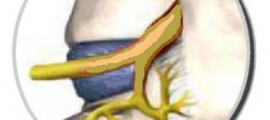
Ramus Communicans Nerve Block (of the Sympathetic Chain)
GENERAL As described more analytically in the chapter of intradiscal degenerative disease, the intervertebral disc is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerve (at each side of the spine) conveying pain signals of nociceptors from the posterior annulus fibrosus (envelope of the disc) to the ramus communicans of the sympathetic chain, then to the posterior spinal […]
-
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block
GENERAL Sphenopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion, no more than 5mm in width, located in the pterygopalatine fossa of the skull. The sphenopalatine ganglion sends nerve fibres to the lacrimal glands, glands of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, palate and upper pharynx. Postganglionic sympathetic fibres and afferent somatosensory branches of the maxillary nerve pass through […]
-
Intraarticular Injections
GENERAL Intra-articular injections are applied to treat articular pain or/and inflammation of traumatic or degenerative aetiology. It is recommended as a therapeutic option when the conservative treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs has failed. Bursitis is a common inflammatory condition affecting the bursae. It is treated with intra-articular or intra-bursal injections. Bursitis may cause pain of the […]
-
Radiofrequency Pain Treatment
GENERAL There are two types of radiofrequency (RF), conventional (CRF) and intermittent or pulsed radiofrequency (PRF). In CRF, a continuous radiofrequency electric field (RFEF) is applied through an electrode to the active tip of a special needle and controlled heat is generated as a result of ion friction. When aimed at some target nerve, this […]
-
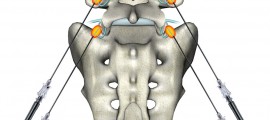
Diagnostic Facet Joint Block
GENERAL Diagnostic facet joint block is a minimally invasive technique that is applied for various diagnostic purposes in patients suffering from chronic lumbar pain and whose clinical examination and history raises the suspicion for facet joint syndrome. DESCRIPTION OF THE TECHNIQUE The diagnostic interventional technique is applied under local skin anaesthesia and fluoroscopic guidance. A […]
-
Superior Hypogastric Plexus Block
GENERAL A superior hypogastric plexus block is used to treat pelvic pain that is resistant to conservative drug therapy. It is also indicated when, despite the efficacy of pharmacotherapy, there are many intolerable drug side-effects (nausea, constipation, sedation etc). ANATOMY Superior hypogastric plexus is a retroperitoneal structure located bilaterally exactly in front of the spine, […]
-
Disc Biacuplasty
GENERAL For many years, chronic discogenic pain due to intradiscal degeneration was treated with conservative therapy that included rest, drugs, physiotherapy and epidural injections having a very brief in duration analgesic effect. Whenever conservative treatment failed, patients would proceed to very high risk surgery of the spine. Disc Biacuplasty (discoplasty of annulus fibrosus) is a […]